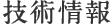Precision vibration isolation technology
The vibration of the floor is used for semiconductor and liquid crystal manufacturing inspection equipment,
Technology not transmitted to precision equipment such as ultra-precision processing machines
What is vibration isolation?
Vibration isolation is the process of preventing the vibration generated from the floor from being transmitted to the onboard equipment.
The equipment is supported by an elastic body to reduce vibration of the floor.
Principle of vibration isolation
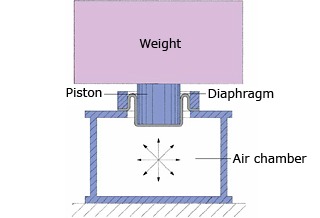
(Fig. 1) Air spring isolation table
Vibration isolation by air spring
- ・If you do not want to transmit floor vibrations to precision equipment, you need to use a vibration isolation table.
- ・In general, the anti-vibration table supports the device with an air spring. (Figure 1)
- ・The anti-vibration table is supported by three or more air springs.
- ・The size of the air spring is determined by the load received by the anti-vibration table.
- ・The softer the air spring (lower the resonance frequency), the higher the performance and the wider the vibration isolation range.
vibration transmissibility
- ・The ratio of the vibration on the anti-vibration table and the vibration on the floor is called the vibration transmissibility. (Figures 2 and 3)
- ・If the vibration transmissibility is greater than 0 dB, it becomes a resonance area and the vibration is amplified.
- ・If the vibration transmissibility is less than 0 dB, it is in the vibration isolation area and the vibration is reduced.
- ・The frequency at which the vibration transmissibility peaks is called the natural frequency.

(Fig. 2) Vibration isolation model
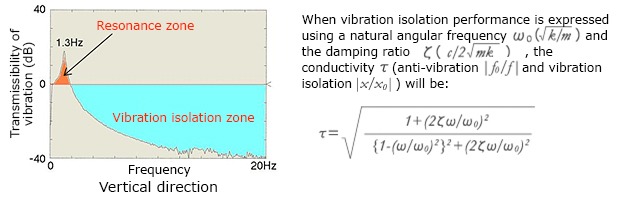
(Fig. 3) Vibration transmissibility formula
Horizontal vibration isolation
- ・There are a total of 6 degrees of freedom for vibration, not only in the vertical direction, but also in the horizontal direction and the rotational direction.
- ・In general diaphragm air springs, the natural frequency in the horizontal direction is several times that in the vertical direction, and it is likely to affect equipment.
- ・It is important to lower the natural frequency of the vibration isolation table not only in the vertical direction but also in the horizontal direction.
Passive unique technology
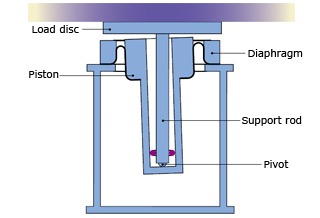
gimbal piston
The stable vibration isolation table incorporates a gimbal mechanism in the piston of the diaphragm air spring.
Features
- ・Compact structure
- ・Soft horizontal spring characteristics can be obtained. A vibration isolation effect equivalent to that in the vertical direction can be obtained.
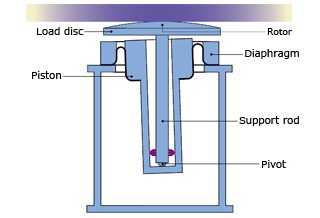
dome gimbal piston
A dome gimbal piston has a much lower spring characteristic than a gimbal piston by providing a spherical rolling element on the top surface of the gimbal piston's load disc.
Gimbal piston 1.2Hz
Dome gimbal piston 0.8Hz
Features
- ・Lower cost and better performance than dual structure.
*Please contact us as it may not be applicable to equipment with a high center of gravity.
Active specific technology
Control of Active Isolation Table
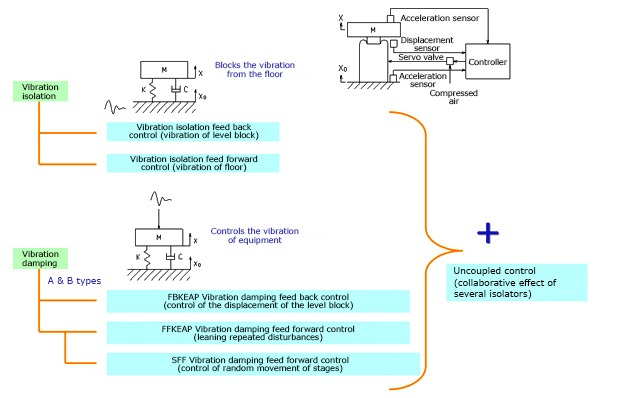
Vibration isolation performance
Vibration isolation is divided into feedback, which detects and controls the vibration of the equipment or surface plate with an accelerometer, and feedforward, which detects and controls vibration of the floor. Kurashiki Kako is equipped with both as standard.
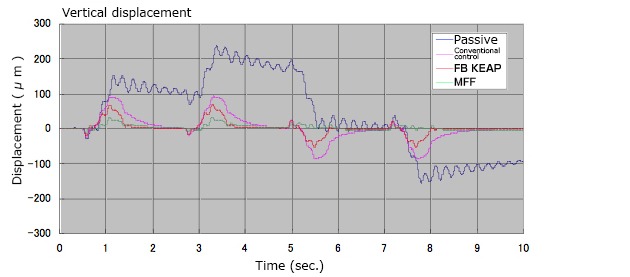
Damping performance
Damping is also roughly divided into feedback and feedforward. Feedback controls the displacement via a displacement sensor. Feedforward is divided into FFKEAP control, which is effective against repeated disturbances, and MFF (Motion Feedforward), which is effective against random disturbances. Feedforward is optional.
Uncoupled control
This control effectively distributes the input signal from the sensor to the four legs without waste.
Vibration isolation performance
The figure above shows an example of performance measured under minute amplitude floor vibration.
By adding active control to the excellent vibration isolation performance of air springs, resonance is eliminated and vibration isolation in the entire frequency range is possible.
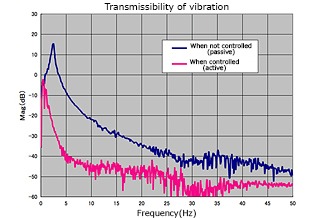
- ・When not controlled (passive)
air spring only - ・During control (active)
Feedback control + feedforward control
Damping for random stage motion
MFF (Motion Feed Forward) is a control method that estimates shaking based on previously input stage movement information when stage movement is random, and starts control before the anti-vibration table or equipment shakes.